レコードの並べ替え
レコードの並べ替えは、Managerクラスの「order by」というメソッドで行います。
<モデル>.objects.<all/filterなど>.order_by(項目名)年齢順に並べ替えてみましょう。
views.pyのindex関数を修正します。
hello/views.py
def index(request):
data = Contact.objects.all().order_by('age') #☆
params = {
'title': 'Hello',
'message':'',
'data': data,
}
return render(request, 'hello/index.html', params)index.htmlも見やすいようにフォーマットを調整します。
hello/templates/hello/index.html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>hello</title>
</head>
<body class="container">
<h1 class="display-4 text-primary">
{{title}}</h1>
<p>{{message|safe}}</p>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>name</th>
<th>age</th>
<th>mail</th>
<th>birthday</th>
</tr>
{% for item in data %}
<tr>
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.age}}</td>
<td>{{item.mail}}</td>
<td>{{item.birthday}}</td>
<tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>webブラウザにてアクセスします。
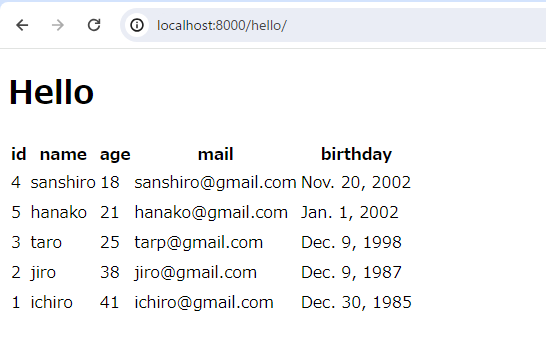
年齢順に並び替えられています。
逆順にする場合は、下記のように定義します。
<モデル>.objects.<all/filterなど>.order_by(項目名).reverse()hello/views.py
def index(request):
data = Contact.objects.all().order_by('age').reverse() #☆
params = {
'title': 'Hello',
'message':'',
'data': data,
}
return render(request, 'hello/index.html', params)werブラウザにてアクセスします。
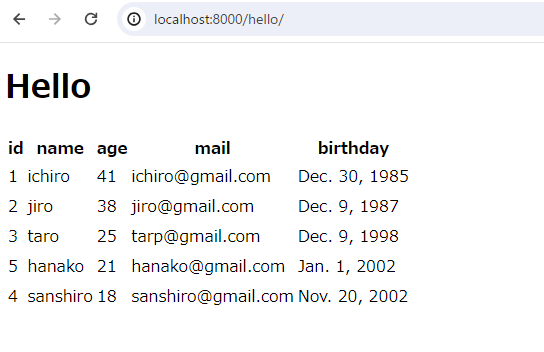
年齢が逆順に並び替えられています。
指定した範囲のレコードを取り出す
レコード数が多い場合、一部のデータのみ取り出す必要が出てきます。
allやfilterなどで取り出されるのはQUerySetというクラスのインスタンスです。
このQuerySetでは下記のように取り出す位置を指定することができます。
<QuerySet>[開始位置:終了位置]それでは実際に位置を指定して取り出してみましょう。
views.pyのfind関数を修正します。
/hello/views.py
def find(request):
if (request.method == 'POST'):
msg = 'search result:'
form = FindForm(request.POST)
find = request.POST['find']
list = find.split()
data = Contact.objects.all()[int(list[0]):int(list[1])] #☆
else:
msg = 'search words...'
form = FindForm()
data =Contact.objects.all()
params = {
'title': 'Hello',
'message': msg,
'form':form,
'data':data,
}
return render(request, 'hello/find.html', params)
find.htmlも見やすいように修正します。
hello/templates/hello/find.html
{% load static %}
<!doctype html>
<html lang="ja">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>{{title}}</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css"
rel="stylesheet" crossorigin="anonymous">
</head>
<body class="container">
<h1 class="display-4 text-primary">
{{title}}</h1>
<p>{{message|safe}}</p>
<form action="{% url 'find' %}" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<tr><th></th><td>
<input type="submit" value="click"
class="btn btn-primary mt-2"></td></tr>
</form>
<hr>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>name</th>
<th>age</th>
<th>mail</th>
<th>birthday</th>
</tr>
{% for item in data %}
<tr>
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>{{item.age}}</td>
<td>{{item.mail}}</td>
<td>{{item.birthday}}</td>
<tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>
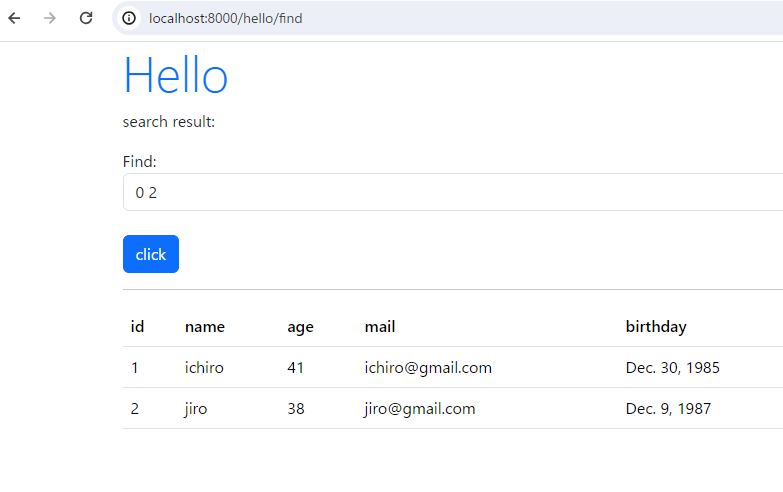
webブラウザにてアクセスします。
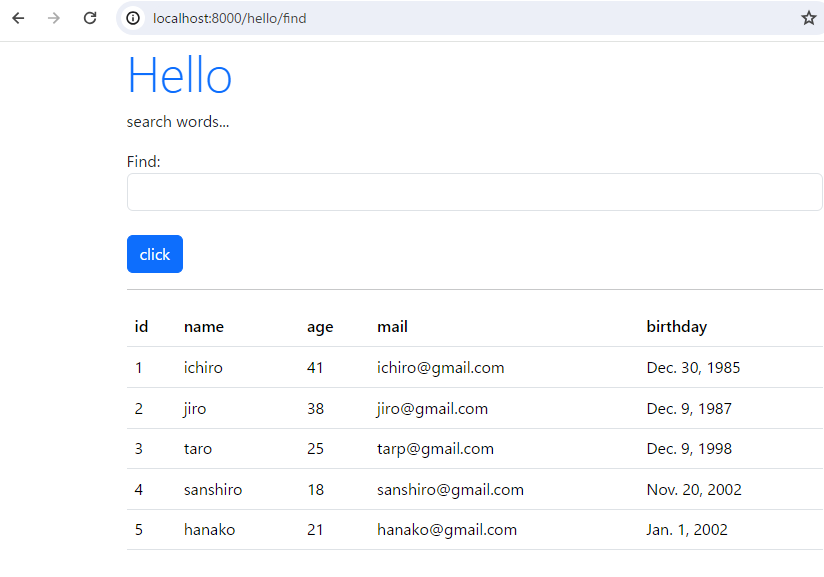
開始位置と終了位置をスペースで区切って入力して、「click」をクリックします。
「0 2」
レコード集計とaggregate
多数の数値データなどを扱う場合、保存してある値を取り出すだけでなく、必要なレコードの値を集計処理することもよくあります。これはaggregateというメソッドで集計を行います。
変換=<モデル>.objects.aggregate(関数)引数に設定する関数には下記の集計関数を用います。
| Count(項目名) | 指定した項目のレコード数を返します |
| Sum(項目名) | 指定した項目の合計を計算します |
| Avg(項目名) | 指定した項目の平均を計算します |
| Min(項目名) | 指定した項目から最小値を返します |
| Max(項目名) | 指定した項目から最大値を返します |
ではageの集計をしてみましょう。
views.pyのindex関数を下記のように修正します。
/hello/views.py
from django.db.models import Count,Sum,Avg,Min,Max
def index(request):
data = Contact.objects.all()
re1 = Contact.objects.aggregate(Count('age')) #☆
re2 = Contact.objects.aggregate(Sum('age')) #☆
re3 = Contact.objects.aggregate(Avg('age')) #☆
re4 = Contact.objects.aggregate(Min('age')) #☆
re5 = Contact.objects.aggregate(Max('age')) #☆
msg = 'count:' + str(re1['age__count']) \
+ '<br>Sum:' + str(re2['age__sum']) \
+ '<br>Average:' + str(re3['age__avg']) \
+ '<br>Min:' + str(re4['age__min']) \
+ '<br>Max:' + str(re5['age__max'])
params = {
'title': 'Hello',
'message':msg,
'data': data,
}
return render(request, 'hello/index.html', params)
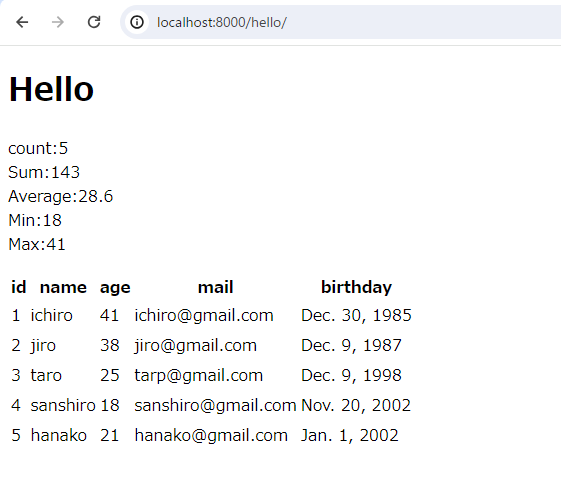
webブラウザにてアクセスします。それぞれ集計されていることが確認できます。
SQLを直接実行する
複雑な検索を行う場合、SQLを使用する必要が出てきます。
これには、Managerクラスのrawというメソッドを使います。
変数=<モデル>.objects.raw(クエリ文)
それでは実際にSQLクエリを実行するサンプルを作ってみましょう。
views.pyのfind関数を修復します。
/hello/views.py
def find(request):
if (request.method == 'POST'):
msg = request.POST['find']
form = FindForm(request.POST)
sql = 'select * from hello_contact'
if (msg != ''):
sql += ' where ' + msg
data = Contact.objects.raw(sql)
msg = sql
else:
msg = 'search words...'
form = FindForm()
data =Contact.objects.all()
params = {
'title': 'Hello',
'message': msg,
'form':form,
'data':data,
}
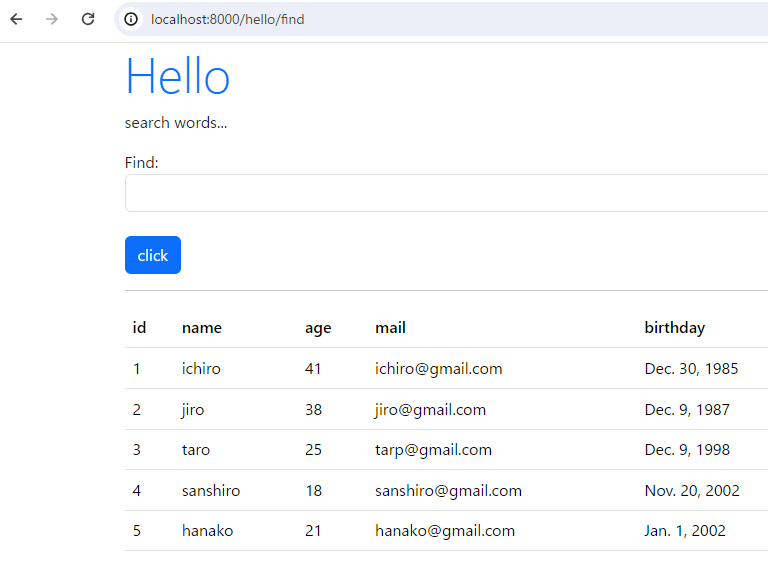
return render(request, 'hello/find.html', params)webブラウザにてアクセスします。allで取得するときと同様のデータが表示されます。
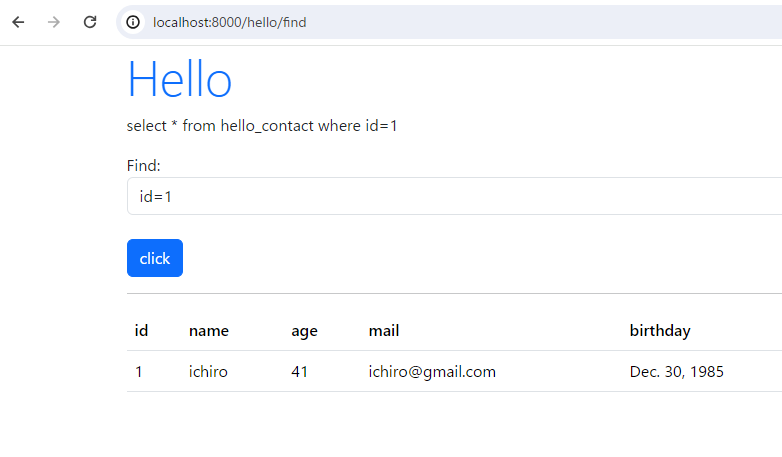
検索条件を追加することも可能です。
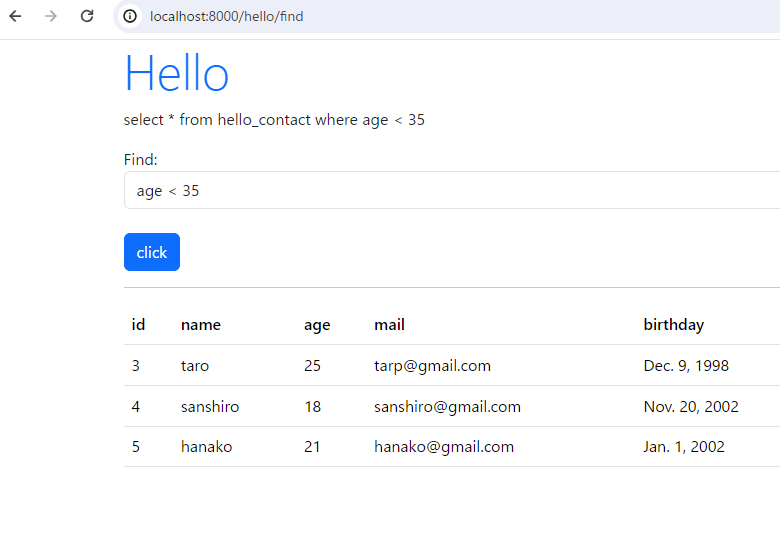
この記事は役に立ちましたか?
もし参考になりましたら、下記のボタンで教えてください。

コメント